
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 National Demonstration Center for Experimental Physics Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
4 e-mail: zhangyaxun@hrbeu.edu.cn
The typical functions of the optical fiber are communication and sensing. However, the fiber functions need to extend to meet the requirements of the development of artificial intelligence. This paper achieves an all-fiber device with storage and logic computing functions using a single-mode fiber and (GST) material. We use the pulse amplitude modulation (the switching energy is about 50 nJ) to switch the GST state for performing the eight-level data storage (3-bit). The all-fiber memory device has the advantages of high optical contrast (about 38%), good reversibility, and high repeatability. We implement the all-optical logic operations (“AND” and “OR”) by using two memory cells in series and parallel. For the first time, we use the single-mode optical fiber to realize storage and computing functions, and this intelligent fiber has tremendous application potential in intelligent optical fiber communication and portends a new paradigm for brain-like computing.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(2): 02000357

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-Fiber Integrated Optics of Ministry of Education, College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 Institute of Applied Physics and Materials Engineering, University of Macau, Avenida da Universidade, Taipa, Macao SAR, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
A multi-focus optical fiber lens is numerically demonstrated based on an all-dielectric metasurface structure. The metasurface consists of an array of rectangular silicon resonators with varying widths in order to obtain the required phase distribution. The core diameter of the multimode fiber is large enough to contain sufficient resonance units. The spatial distribution of the dielectric resonators is dictated by spatial multiplexing, including interleaving meta-atoms and lens aperture division, to achieve multi-focus properties. The proposed optical fiber metalens can produce two or three focal points along the longitudinal direction with high focusing efficiency. The size of every focal point is close to the diffraction limit, and the relative intensity on each focus can be controlled by adjusting the number of the respective resonators. The proposed optical fiber lens will have a great potential in the fields of integrated optics and multifunctional micro/nano devices.
multi-focus lens optical fiber metasurface Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(5): 050601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 National Demonstration Center for Experimental Physics Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
4 e-mail: liuzhihai@hrbeu.edu.cn
Light is a precious resource that nature has given to human beings. Converting green, recyclable light energy into the mechanical energy of a micromotor is undoubtedly an exciting challenge. However, the performance of current light-induced micromotor devices is unsatisfactory, as the light-to-work conversion efficiency is only . In this paper, we propose and demonstrate a laser-induced rotary micromotor operated by -type photopheresis in pure liquid glycerol, whose energy conversion ratio reaches as high as , which is 3–6 orders of magnitude higher than that of previous light-induced micromotor devices. In addition, we operate the micromotor neither with a light field carrying angular momentum nor with a rotor with a special rotating symmetrical shape. We just employ an annular-core fiber to configure a conical-shaped light field and select a piece of graphite sheet (with an irregular shape) as the micro-rotor. The -type photophoretic force introduced by the conical-shaped light field drives the rotation of the graphite sheet. We achieve a rotation rate up to 818.2 r/min, which can be controlled by tuning the incident laser power. This optical rotary micromotor is available for twisting macromolecules or generating vortex and shear force in a medium at the nanoscale.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(4): 04000534

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 National Demonstration Center for Experimental Physics Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
We propose and demonstrate a dual-channel microfluidic sensor based on a side-hole fiber (SHF) with two long-period fiber grating (LPFG) structures. There are two air holes in the SHF, which are natural microfluidic channels. We fabricate two LPFGs (long-period gratings LPG-A and LPG-B) in the SHF with the resonance wavelengths of 1268.7 nm and 1385.8 nm, respectively. Results show that the refractive index sensitivities of LPG-A and LPG-B are ?76.0 nm/RIU and ?71.1 nm/RIU, respectively. One can measure the refractive index of liquid samples in two channels simultaneously. The proposed dual-channel microfluidic sensor has advantages of good linearity response, fluidic technology compatibility, and easy light input/output coupling and system integration, which helps the sensor to have a potential application in environmental detection and food safety detection.
long-period grating optical fiber sensor refractive index measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 020601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 National Demonstration Center for Experimental Physics Education, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
3 Photonics Research Center, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
We propose and demonstrate single fiber dual-functionality optical tweezers based on a graded-index multimode fiber. By using the multi-angle fiber grinding and polishing technology, we fabricate the multimode fiber tip to be a special tapered shape, contributing to focus the outgoing beam with a large intensity gradient for the first functionality—three-dimensional contactless trapping of a microparticle. By adjusting the radial direction offset between the lead-in single mode fiber and the graded-index multimode fiber, we perform the second functionality—axial shift of the trapped microparticle with respect to the fiber tip without need of moving the fiber probe itself. It is convenient for practical applications. The theoretical and experimental results about the relationship between the radial offset and the equilibrium positions of the microparticle have the good consistency. Tailoring the trap and axial shift of the microparticle based on the graded-index multimode fiber provides convenient avenues for fiber optical tweezers applied in practical researches.
350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(5): 053501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-Fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry of Education, College of Science, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2 Photonics Research Center, School of Electric Engineering and Automation, Guilin University of Electronics Technology, Guilin 541004, China
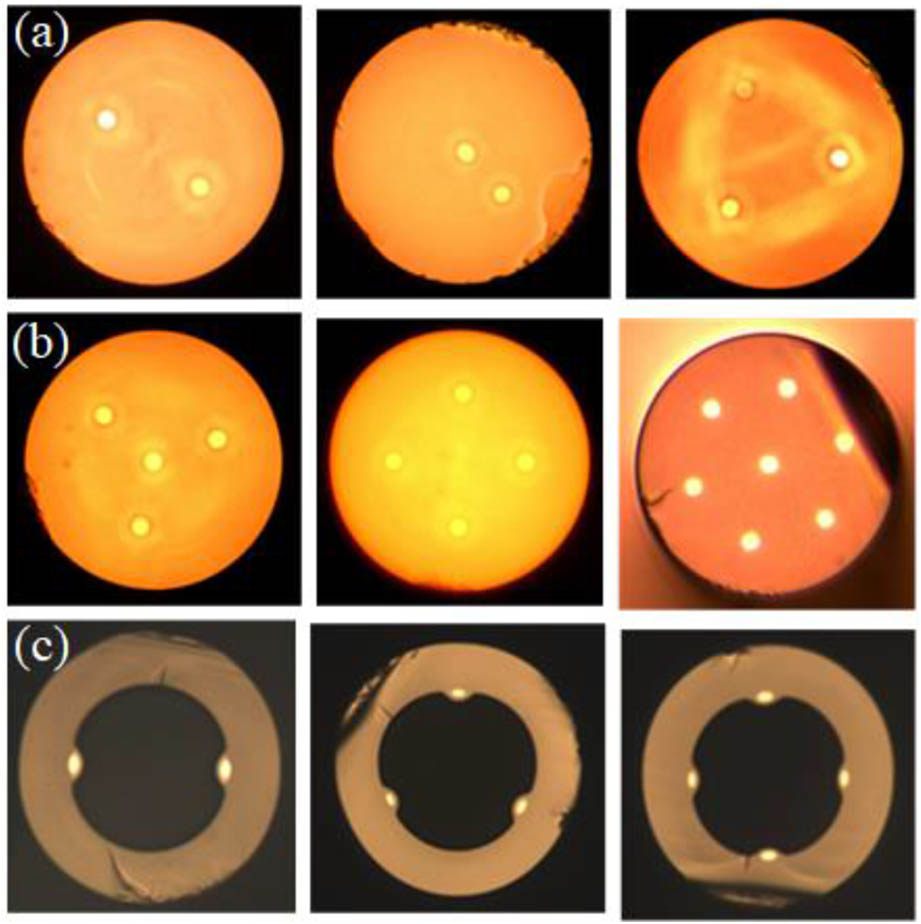
In-fiber integrated optics is an attempt to use silica fiber as a substrate, integrating various optical paths or optical components into a single fiber, to build a functional optical device or component, and to realize a micro optical system, achieving various functions. In-fiber integrated optics is expected to be a new branch of photonics integration. This integration technique enables convenient light beams control and manipulation inside in one fiber. It also provides a research platform with micro and nano scale for interaction between light wave and microfluidic materials. In this review, we briefly summarize the main ideas and key technologies of the in-fiber integrated optics by series integration examples.
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.4005 Microstructured fibers 130.3120 Integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(11): 110601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Lab of In-fiber Integrated Optics, Ministry Education of China, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
We propose and demonstrate a novel single fiber optical tweezer based on a graded-index multimode fiber (GIMMF), which works with a free length GIMMF (>30 cm). We achieve a three-dimensional stable trap of yeast cells by using the GIMMF optical tweezers. Compared with the single-mode fiber optical tweezers, the GIMMF optical tweezers possess large optical trapping forces. Owing to the freedom of the GIMMF length, the fabrication of the GIMMF optical tweezers is simple, repeatable, and highly efficient. The GIMMF tweezers have the penitential to become a new member of the single fiber optical tweezers family and have a wide range of applications in the medical and biological cytology fields.
140.7010 Laser trapping 350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(6): 061402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of In-fiber Integrated Optics of Ministry Education of China, Harbin Engineering University,Harbin 150001, China
2 National Engineering Laboratory for Fiber Optic Sensing Technology, Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430074, China
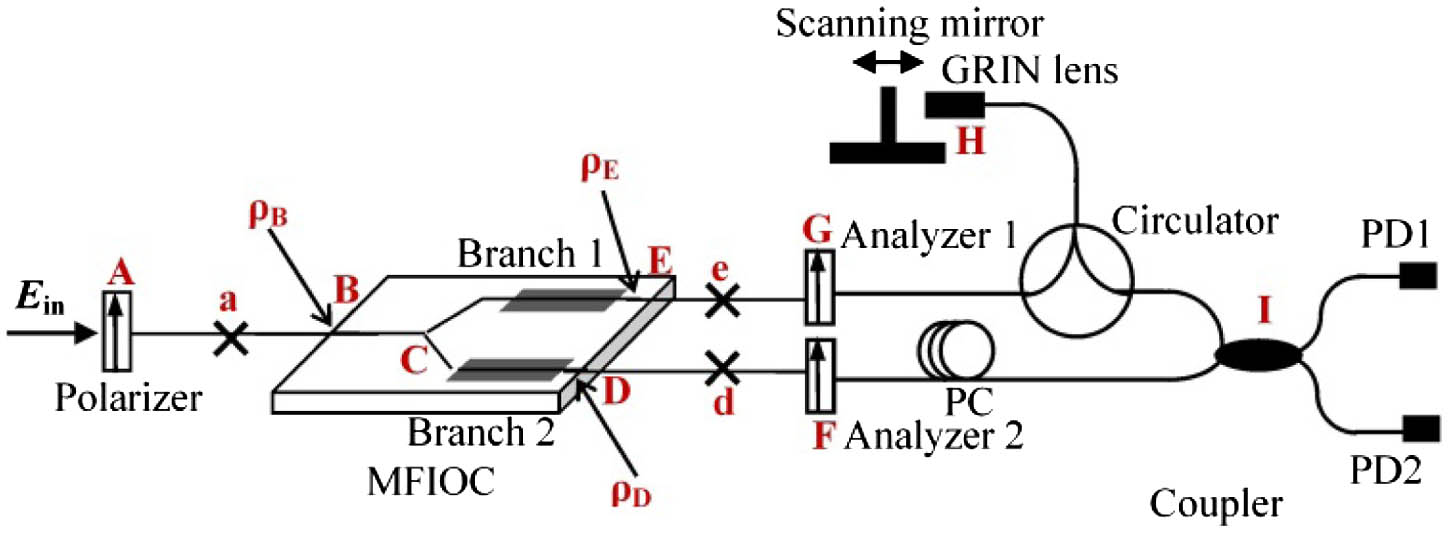
We propose an ultra-simple dual-channel configuration for simultaneously evaluating two branches of a multifunctional integrated optic chip (MFIOC). In the configuration, the MFIOC is employed as a beam splitter to construct the demodulation interferometer together with a 2 × 2 fiber coupler. Interference happens between polarization modes traveling through different channels of the MFIOC. The cross-couplings of each channel are respectively characterized by the interference peaks which distribute on opposite sides of the central interference peak. Temperature responses of the MFIOC are experimentally measured from ?40°C to 80°C. Results show that the proposed configuration can achieve simultaneous dual-channel transient measurements with resolution of ?90 dB and dynamic range of 90 dB. In addition, the two channels of the configuration have consistent measuring performance, and the two branches of the MFIOC have different responses to temperature variation.
Interferometry Interferometry Ellipsometry and polarimetry Ellipsometry and polarimetry Metrological instrumentation Metrological instrumentation Photonics Research
2015, 3(4): 04000115
哈尔滨工程大学理学院光子研究中心, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
提出并制造一种新颖的椭圆芯中空光纤,采用热极化方法使其具有高二阶非线性,可用作相位调制器。该光纤在300 ℃温度、大于1×108 V/m强电场和9 cm有效电极长度条件下热极化30 min后,产生大的线性电光相移。基于双椭圆芯中空光纤构建一种纤内马赫曾德尔干涉仪,通过观察干涉条纹的移动来评估相移,最终得到1.16 pm/V的高二阶非线性系数和0.52 pm/V的线性电光系数。该技术具有简单、灵活的特点,可以用来制作高电光系数器件,降低制作成本,并能进一步提高全光纤器件的集成度。
光纤光学 椭圆芯光纤 二阶非线性 热极化 纤内马赫曾德尔干涉仪 电光器件
哈尔滨工程大学理学院光子科学与技术研究中心, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
通过将单芯单模光纤与多芯光纤纤芯对准熔接后,再在多芯光纤任意位置进行热熔融拉锥,实现多芯光纤光功率的高效耦合注入和光功率在各个纤芯中分布比例的控制,解决了由于多芯光纤结构特殊引起的光源光功率难于直接注入的问题。基于光纤耦合模式理论建立多芯光纤各纤芯之间的耦合模方程,得到各个纤芯中光功率变化与耦合长度之间的变化曲线,并与实际耦合实验结果对比,验证此方法的可行性。研究结果可为多芯光纤光学器件的发展提供潜在的应用价值。
光纤光学 多芯光纤 光功率分布控制 耦合模式理论 光纤器件 中国激光
2011, 38(12): 1205002





